Scientists from the College of Washington and the University of California, Berkeley have performed experiments that calculated the physical limits for the existence of liquid drinking water in icy extraterrestrial worlds. This blend of geoscience and engineering was done to help in the lookup for extraterrestrial lifestyle and the impending robotic exploration of oceans on moons of other planets.
The effects had been not too long ago revealed in Cell Stories Physical Sciences.
“The a lot more a liquid is stable, the much more promising it is for habitability,” stated co-corresponding creator Baptiste Journaux, an performing assistant professor of Earth and area sciences at the UW. “Our success show that the cold, salty, significant-force liquids identified in the deep ocean of other planets’ moons can stay liquid to considerably cooler temperature than they would at reduce pressures. This extends the variety of doable habitats on icy moons, and will allow us to pinpoint the place we really should look for biosignatures, or signals of lifetime.”
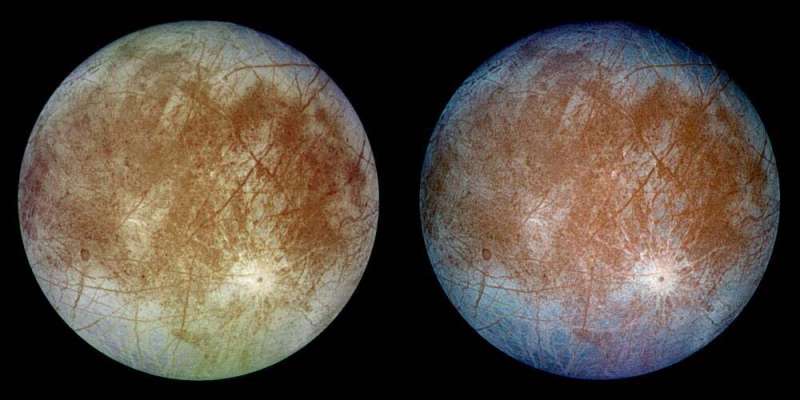
Jupiter and Saturn’s icy moons—including Europa, Ganymede and Titan—are leading candidates inside of our photo voltaic system for hosting extraterrestrial daily life. These ice-encrusted moons are believed to harbor monumental liquid oceans, up to various dozen instances the quantity of oceans on Earth.
“In spite of its designation as the ‘blue marble,’ Earth is remarkably dry when when compared to these worlds,” Journaux stated.
The oceans on these moons may well contain many types of salts and are expected to selection from about 100 miles deep, on Europa, to extra than 400 miles deep, on Titan.
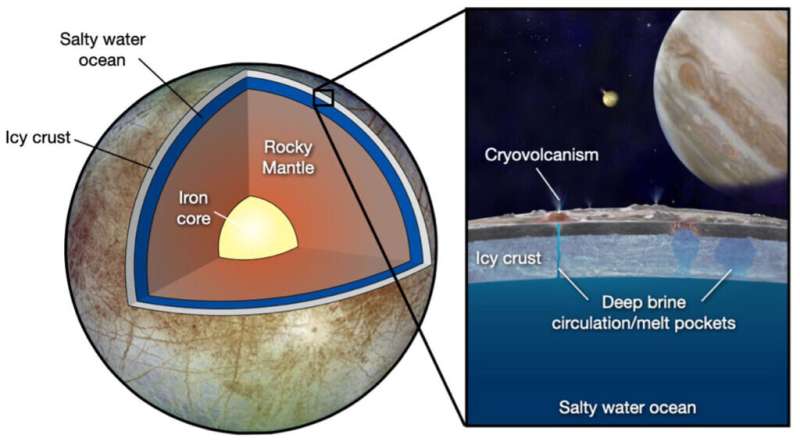
“We know that water supports lifetime, but the major portion of the oceans on these moons are possible underneath zero degrees Celsius and at pressures higher than something expert on Earth,” Journaux claimed. “We necessary to know how chilly an ocean can get just before fully freezing, including in its deepest abyss.”
The analyze centered on eutectics, or the most affordable temperature that a salty option can continue being liquid right before entirely freezing. Salt and drinking water are one example—salty water continues to be liquid below the freezing temperature of pure drinking water, one particular of the reasons persons sprinkle salt on roadways in winter season to stay away from the development of ice.
The experiments made use of UC Berkeley products initially made for the potential cryopreservation of organs for medical applications and for food stuff storage. For this study, nevertheless, the authors employed it to simulate the conditions believed to exist on other planets’ moons.
Journaux, a planetary scientist and pro on the physics of h2o and minerals, labored with UC Berkeley engineers to exam options of 5 diverse salts at pressures up to 3,000 occasions atmospheric tension, or 300 megapascals—about a few situations the stress in Earth’s deepest ocean trench.
“Realizing the cheapest temperature possible for salty water to keep on being a liquid at higher pressures is integral to understanding how extraterrestrial lifetime could exist and prosper in the deep oceans of these icy ocean worlds,” stated co-corresponding author Matthew Powell-Palm, who did the get the job done as a postdoctoral researcher at UC Berkeley, also co-founder and CEO of the cryopreservation enterprise BioChoric, Inc.
Journaux just lately commenced doing the job with NASA’s Dragonfly mission staff, which will mail a rotorcraft in 2027 to Saturn’s most significant moon, Titan. NASA also is leading the Europa Clipper mission in 2024 to explore Europa, just one of the lots of moons orbiting Jupiter. In the meantime, the European Room Agency in 2023 will mail its JUICE spacecraft, or Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer, to take a look at three of Jupiter’s biggest moons: Ganymede, Callisto and Europa.
“The new information obtained from this study could assistance more researchers’ understanding of the sophisticated geological processes observed in these icy ocean worlds,” Journaux reported.
Hubble finds proof of persistent water vapor in a single hemisphere of Europa
Brooke Chang et al, On the pressure dependence of salty aqueous eutectics, Cell Stories Actual physical Science (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrp.2022.100856
Citation:
Experiments measure freezing place of extraterrestrial oceans to support research for daily life (2022, Could 3)
retrieved 4 May perhaps 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-05-extraterrestrial-oceans-assist-everyday living.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Apart from any honest working for the reason of personal review or investigation, no
portion could be reproduced with out the prepared permission. The written content is presented for information and facts reasons only.